What is SD-WAN? Everything you need to know.
Here’s what we’ll look at:
22 minute read time
What is SD-Wan?
A software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) is a method of networking that routes traffic dynamically across distributed branches and remote locations using software intelligence.
By using software-defined (SDN) technology, SD-WAN separates network logic and configuration from physical connections and hardware, allowing it to create a centrally managed virtual WAN that connects remote branches and locations regardless of the connection type, access point or carrier.
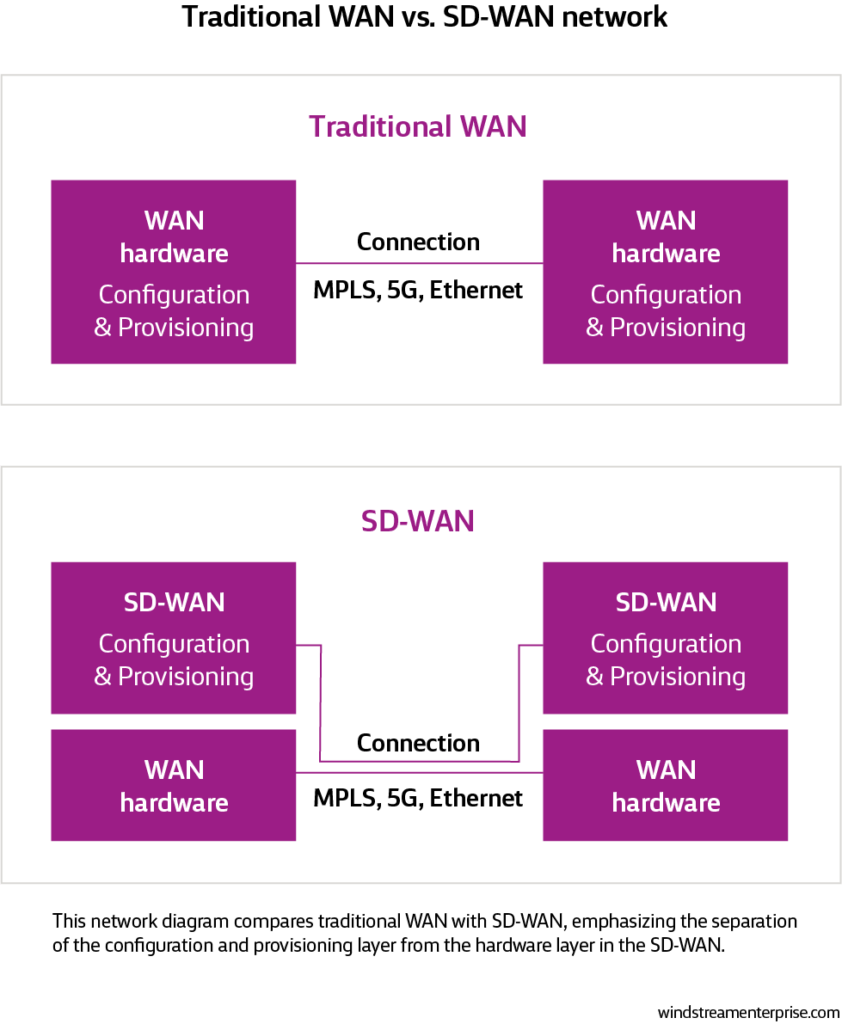
What is SD-WAN used for?
SD-WAN simplifies network management by abstracting and automating tasks traditionally set manually on edge devices, which allows IT to configure, manage, monitor and secure most aspects of the WAN, including edge devices and traffic flows.
Since SD-WAN abstracts the transport layer from hardware to software, IT can prioritize network traffic and use more affordable public or private links like broadband or wireless in conjunction with Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS).
What does SD-WAN deliver?
For enterprises that want to move applications and processes to the cloud, SD-WAN offers key advantages such as:
-
100% uptime
-
Improved app performance
-
Flexible connectivity
-
Enhanced security
-
Centralized management
-
Visibility and co-managed control
-
Reduced costs
SD-WAN vs. SDN
SD-WAN focuses on providing software-defined application routing to the wide area network, and on connecting an organization’s geographically distributed locations on a national or global basis. In contrast, SDN is primarily focused internally, within the LAN or within the service provider’s core network. Also, while SD-WAN is built on SDN technology, the programming is handled behind the scenes by the SD-WAN vendor, eliminating the complexity for the end user. SDN is programmable by the customer or user. To learn more, read this article on the differences between SD-WAN and SDN.
6 key features of SD-WAN
For distributed enterprises that rely on cloud applications and support remote work, SD-WAN’s automation, centralization and flexibility deliver:
Agility:
Enterprises can pivot rapidly and change operational models, such as shifting workloads to the cloud to enable remote work.
Scalability:
IT can add more capacity where it’s needed—and reduce capacity where it’s not— which is crucial for supporting a remote workforce and opening new sites rapidly.
Security:
As organizations move from private MPLS environments to Ethernet Internet, broadband and cellular broadband, security becomes more important—since a fluid hybrid work environment means more entry points into the network. SD-WAN enables cloud-based firewalls and rulesets which help organizations apply the same security policies to all end users, regardless of location.
Manageability:
SD-WAN offers centralized management with better visibility and control from a single portal, which gives IT a clear view into network performance and the ability to make changes as needed.
Bandwidth optimization:
SD-WAN monitors and selects the best-performing network paths for better app performance, which allows IT to leverage more cost-effective transport methods (like Internet broadband) that provide maximum network capacity and reliability at lower costs.
Cloud access:
In a cloud-centric world, SD-WAN is ideal for global enterprises. Since SDN determines optimal routing paths, SD-WAN provides better application performance with optimized cloud connectivity and simplified management.
Gartner estimates that 60% of the enterprises they surveyed will have implemented the technology by 2024.1
Why SD-WAN? Why now?
With the explosion of remote work and accelerated digital transformation, the need for reliable networks and connectivity has never been higher. Many organizations are looking for network solutions that offer the flexibility and security to support cloud-based applications and services—along with rock-solid continuity and uptime to ensure better employee and customer experiences.
These businesses are discovering that they can no longer rely on outdated legacy access technologies like MPLS, Time Division Multiplexing (TDM), DS1 and DS3 access solutions, or services like primary rate interfaces (PRIs) and plain old telephone services (POTS). They’re turning to SD-WAN as a highly agile option that lets them tailor network bandwidth at their locations as they shift their business and operational models.
SD-WAN vs. MPLS
MPLS was once the VPN of choice for distributed enterprises, but the growth in cloud computing—and the subsequent explosion in bandwidth demand—pushed traditional MPLS networks to their limits.
This shift was accelerated by the global pandemic as public cloud vendors stepped up to provide applications and services that helped companies stay afloat while they reorganized their remote workforces, reconfigured their supply chains and developed new ways to stay connected to their customers.
With this shift towards the cloud, enterprises quickly discovered that downtime is no longer an option, as it can lead to catastrophic losses in productivity and revenue. They discovered that SD-WAN can leverage MPLS connections, as well as more cost-effective and higher bandwidth access types—making it a cost-effective upgrade option that minimizes CAPEX outlay.
Additionally, they found that SD-WAN doesn’t rely on the traditional hub and spoke WAN model, which allows for faster, more efficient application performance.
Ultimately, businesses determined that SD-WAN can be less expensive, more secure and provide higher uptime compared to MPLS. The table below breaks down the differences in more detail.
For a deeper understanding of the differences between these two technologies, see SD-WAN vs. MPLS: what’s the difference and which is better?
SD-WAN vs. MPLS: a comparison
| CRITERIA | SD-WAN | MPLS |
|---|---|---|
| Provisioning time | Low: low-touch via portal | High: manual |
| Management | Centralized | Decentralized |
| Application-level visibility | High | Low |
| Bandwidth scaling | Immediate | Time-consuming |
| Resiliency | High: cost effective | Low: expensive to add |
| Security | High when used with IPSec and SASE-type services (See SD-WAN and security below) | Good due to dedicated, private access |
| Geographical reach | Scalable from its ability to work over a variety of networking types | Limited by the reach of the MPLS provider |
| Cost | Lower due to use of Internet broadband | Higher from dedicated lines |
How SD-WAN works
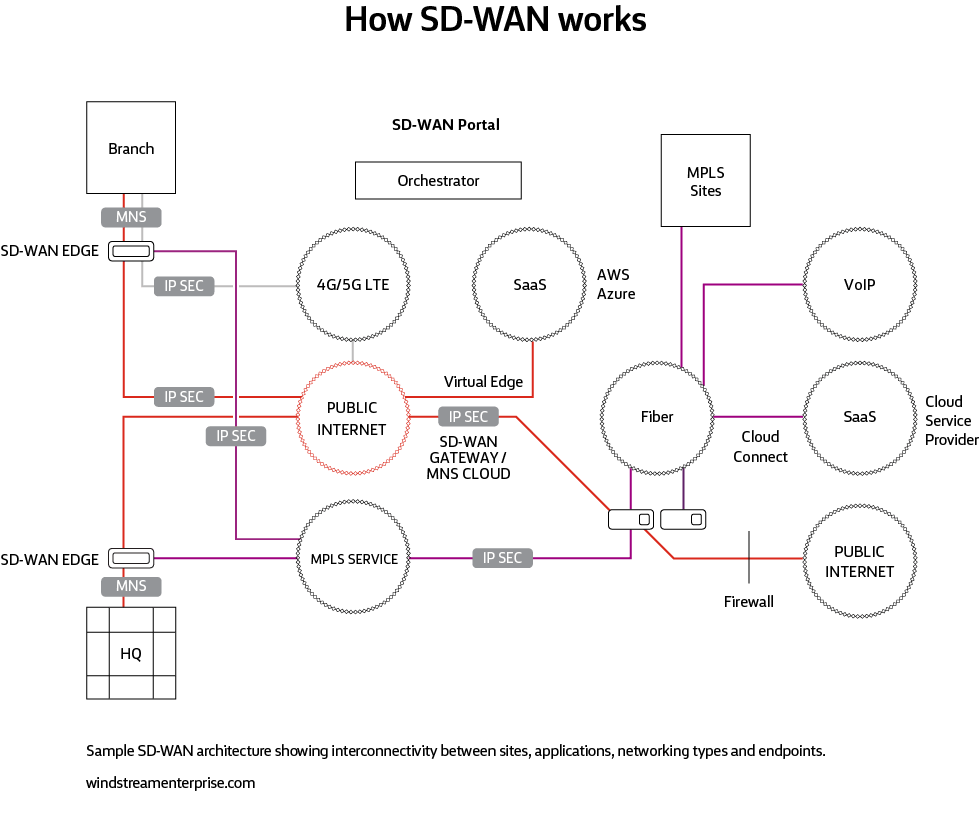
SD-WAN architecture relies on virtualized overlays that make it easier to implement and replicate policies among distributed edge devices—reducing the time, complexity and potential for human error when adding capabilities such as application prioritization and security settings. SD-WAN automatically detects network conditions and provides dynamic path steering and forward error correction to ensure high-priority apps get the performance they need.
For an in-depth look at how SD-WAN works, download our eBook: SD-WAN for Dummies
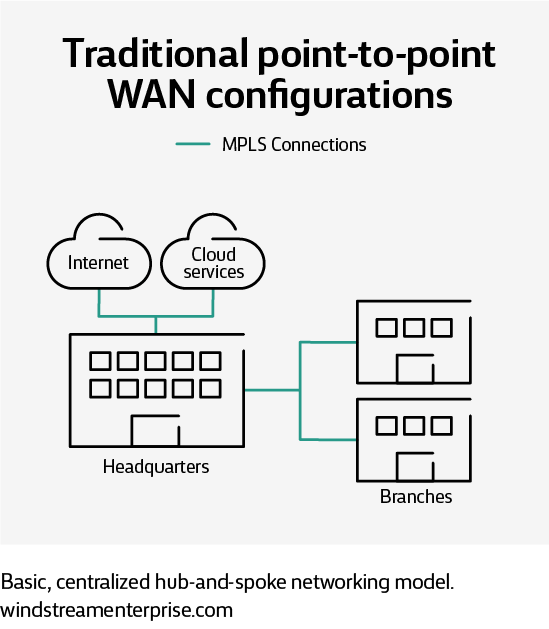
Connectivity options for SD-WAN
Traditional point-to-point WAN configuration
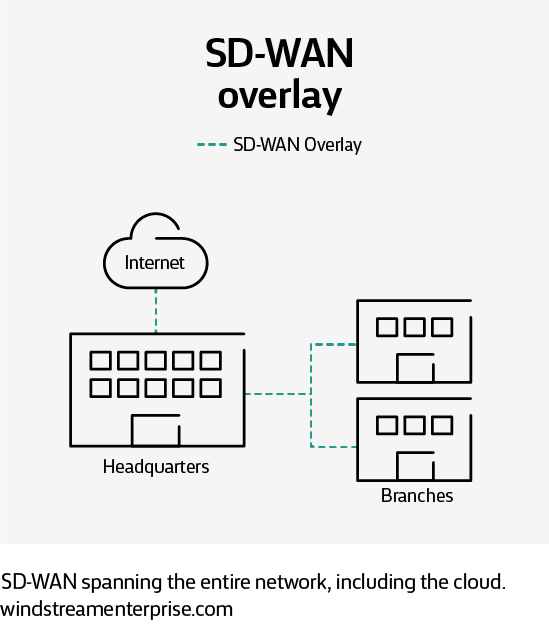
SD-WAN overlay
Multipath SD-WAN with various transports
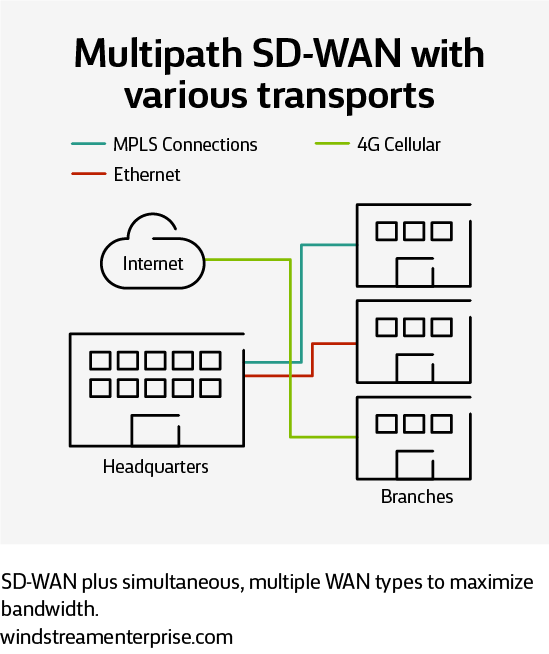
Multipath SD-WAN with redundancy
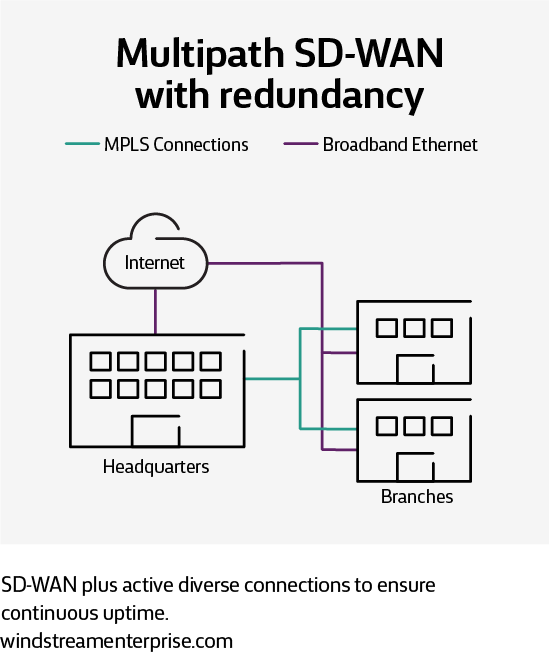
Multipath SD-WAN with data pathing
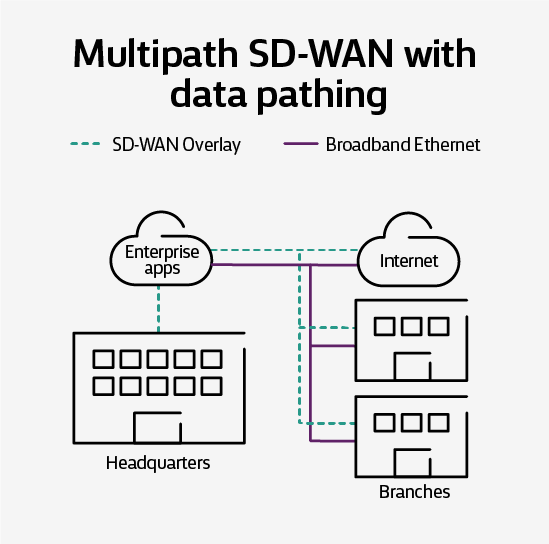
Remote branch direct Internet connection
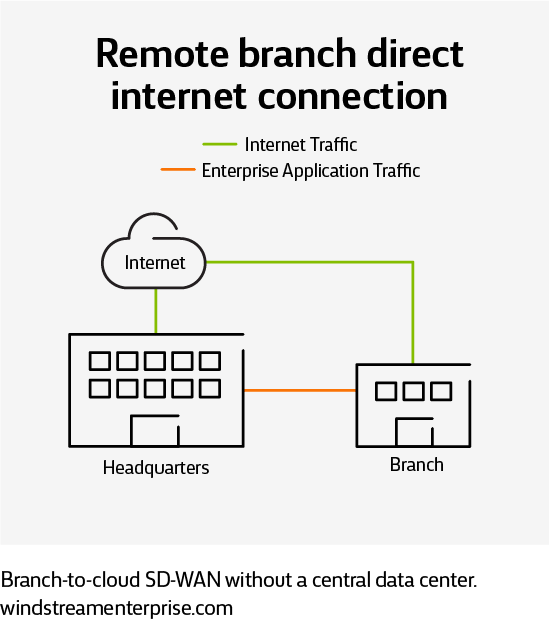
Cloud-based SD-WAN
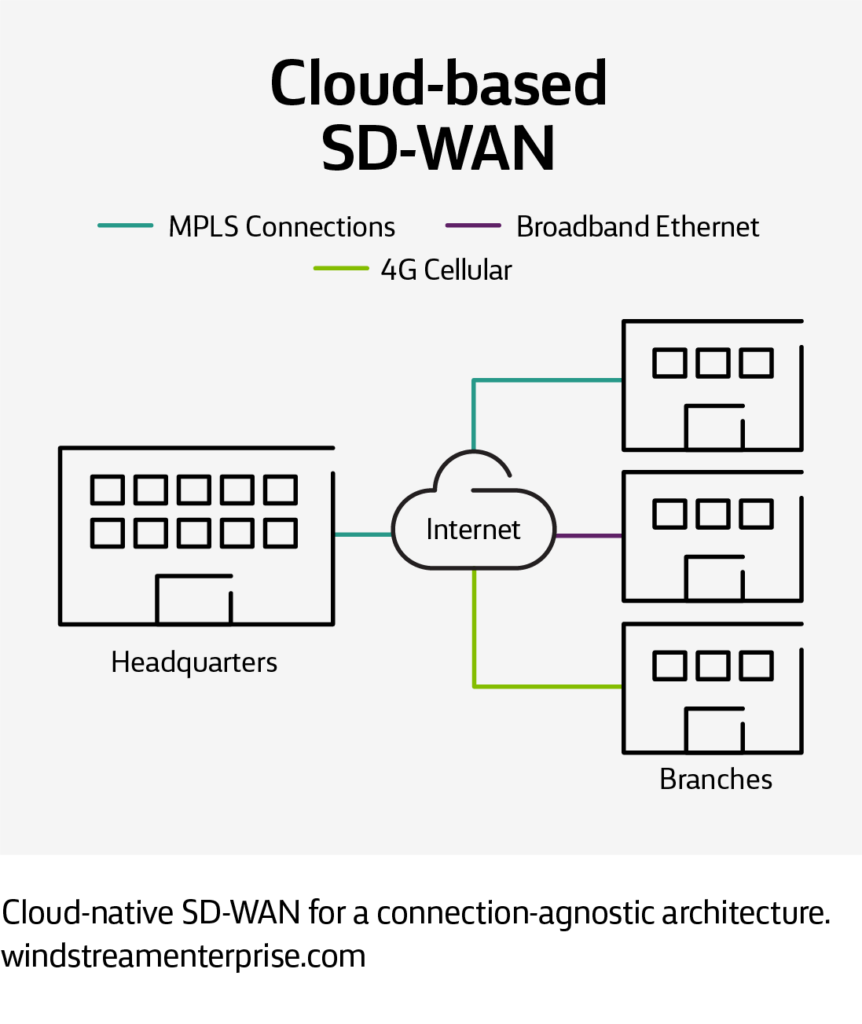
9 key benefits of SD-WAN
SD-WAN solves the business challenges of cloud networking, digital transformation and remote work by delivering these benefits:
-
Simple to use:
SD-WAN lets IT control the entire WAN through one interface. Network upgrades take minutes instead of days with the centralized management portal, which eliminates the need for technicians to perform time-consuming installations at each location.
-
Enhanced experiences:
Reliable access to cloud-based applications helps enhance customer experiences and improve employee productivity.
-
Onramp to SASE:
Secure access service edge (SASE) is built on the solid foundation of SD-WAN, intertwined with software intelligence, which enables optimal WAN management. This allows employees to use their unified communications tools, as well as access business applications seamlessly and securely from any location.
-
Higher performance:
Applications and networks perform smoother, with less downtime, on SD-WAN. Data travels across several different channels simultaneously while using the quickest routes, thanks to dynamic bandwidth allocation. Moreover, IT has greater control over bandwidth prioritization for critical applications.
-
Reduced downtime:
IT gains a single interface for all network insights, provisioning and management. This ensures immediate action on network issues. If one path fails, dual active uplinks ensure a seamless transition to a secondary link, resulting in virtually no downtime.
-
Reliability:
In addition to providing optimized cloud access, SD-WAN also provides remote access to resources on site. As a result, cloud-based applications like Salesforce and Microsoft Office 365 are more reliable.
-
Flexibility:
SD-WAN allows the freedom to choose from a mix of access providers and transport types to enable hybrid networking.
-
Better visibility and co-managed control:
SD-WAN offers IT managers deeper visibility of their entire network—including branches, headquarters and the cloud. Additionally, IT has more granular control over application prioritization and bandwidth allocation, allowing them to make changes on the fly without the need for truck rolls or intervention from the bandwidth provider.
-
Cost efficiency:
Enterprises can realize significant savings on bandwidth use as SD-WAN supports cost-effective, readily available high-bandwidth broadband Internet.
SD-WAN and security
By 2025, at least 60% of enterprises will have explicit strategies and timelines for SASE adoption, up from 10% in 2020.2
Following the surge in remote work at the beginning of this decade, organizations are more reliant on systems and technologies operating outside of an official office structure. From an IT perspective, the perimeter is no longer limited to a location. Now, it’s a set of dynamic edge capabilities delivered from the cloud when needed.
Additionally, cyberthreats have become more serious. The constant stream of breaches, DDoS attacks and more are a danger to organizations that fail to adequately protect their cloud-based devices, applications, services and data. Any plan to adopt SD-WAN then, should factor in security.
SASE and SD-WAN
Check out this SD-WAN security checklist to compare security functions by solution set to help make the most informed decision for your business.
Forward-looking organizations are turning to secure access service edge (SASE), an emerging “as a Service” framework that builds on the strengths of SD-WAN, to deliver protected networking and security services. While most SD-WANs include a built-in stateful firewall, and can be supported by managed network security services, they also offer a solid foundation for SASE.
SASE dynamically extends the edge of the private network right up to multiple clouds such as AWS, Azure and Google Cloud Platform and to popular SaaS applications. For end users, this provides a virtual onramp to those cloud providers’ services.
When combined with network security technologies like Firewall as a Service (FWaaS), Secure Web Gateways (SWG), Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), SD-WAN’s software intelligence allows users to access data and applications seamlessly and securely from any location with any device. Policies for those technologies can be managed and orchestrated by the organization from the cloud.
SASE also provides an ideal platform for secure unified communications applications including voice, video and chat. And by incorporating a SASE framework with SD-WAN during migration, IT has a proven foundation for adopting new security technologies as they are introduced.
To learn more about bringing robust SASE to your organization with SD-WAN, download this brochure: The Convergence of SD-WAN and Security
SD-WAN and costs
As more enterprises shift to cloud economics, in which costs shift from dedicated, on-premises equipment to an as-a-service model, SD-WAN allows them to combine application performance, access and security into a single solution—resulting in efficiencies they couldn’t achieve using traditional standalone appliances and secure remote access technologies.
The ongoing cost benefits of SD-WAN come mainly from savings on access connections and the convergence of voice services.
Access savings
For many enterprises, MPLS circuits are prohibitively expensive. SD-WAN offers lower-cost access replacements to MPLS connections. Adding new bandwidth via cost-effective Internet broadband to augment or replace MPLS is simple. And businesses can achieve considerable savings on voice costs by eliminating legacy on-premises private branch exchange (PBX), PRI and POTS lines.
Operational savings
By adopting SD-WAN, companies can avoid lost revenues and productivity by minimizing network outages. What’s more, they can ensure the quality of service (QoS) of connections to cloud services and applications—as well as high availability connections to WAN sites. And SD-WAN’s centralized management capabilities reduce the need (and costs) for on-site provisioning and maintenance.
3 SD-WAN best practices
What’s the key to a successful SD-WAN implementation? Like any large technology solution rollout, getting SD-WAN right is all about upfront strategy and planning. Follow these best practices to ensure a successful implementation for your software-defined wide area network:
1. Align on your what and why
The basis for SD-WAN success lies in your ability to understand your organization’s needs today, and anticipate what you might need going forward. Ask yourself and your stakeholders:
-
What business challenge is SD-WAN trying to solve?
-
What opportunity are we trying to capitalize on?
-
How is technology inhibiting us today?
2. Identify your who
Once you’ve determined that SD-WAN is right for your business and aligned with your buying committee, you’ll need to determine who will design, procure, install and ultimately manage your solution—your team or a managed service provider.
3. Pinpoint your where and when
Once you’ve determined who will design, install and manage SD-WAN in the long run, you need a migration plan. Understanding exactly what you have in place now—as well as what you might need in six months, one year, three years—will help avoid hang-ups like project delays and budget overruns.
For more guidelines, see our complete set of SD-WAN best practices for a successful implementation.
Managed versus do-it-yourself (DIY) SD-WAN
Compared to traditional WAN technology, SD-WAN is a completely different model. Defining and implementing the right SD-WAN solution for a particular organization requires a specialized skill set.
Even IT departments that have successfully installed SD-WAN themselves have found that it’s a major undertaking, and tend to value third-party assistance as they gain experience.
By working with a dedicated SD-WAN service provider, IT departments can circumvent many of the challenges they encounter during an SD-WAN migration. A third-party service provider with a proven track record of successful deployments can complement the IT team by handling access configuration, bandwidth prioritization and endpoint installations—along with security and multiple connectivity types.
This can save the enterprise the trial-and-error time (and expense), as well as provide IT with the single point of contact “one-back-to-pat/one-throat-to-choke” in the event of network issues.
11 questions to ask before deploying an SD-WAN solution yourself
If you are considering setting up an SD-WAN, here’s a list of things to consider:
-
How critical is time to solution?
-
Have I taken full stock of my existing inventory including sites, equipment and users?
-
What am I spending today on bandwidth?
-
What am I prepared to use for redundant connections?
-
What is my capability to integrate SD-WAN into my legacy WAN?
-
Do I have access to skilled SD-WAN resources?
-
Do I want to manage multiple providers for diverse access?
-
Does my organization favor CAPEX or OPEX spending?
-
How important is a “single pane of glass” management console?
-
What Service Level Agreements am I prepared to support?
-
How much resiliency is needed in my SD-WAN deployment?
For a deeper dive, read this article on questions to ask before deploying SD-WAN
SD-WAN from Windstream Enterprise
Industry Recognition
2021 TMCnet INTERNET TELEPHONY
Product of the Year: SD-WAN
2020/2019 TMCnet INTERNET TELEPHONY
Award for SD-WAN Provider of the Year
2020 MEF SD-WAN Award
North America Product of the Year
As an analyst-recognized leader in product innovation, Windstream Enterprise offers award-winning managed SD-WAN ConciergeTM that stands apart in the industry. Windstream Enterprise has partnered with three of the leading SD-WAN technology providers, VMware, Fortinet and Cato Networks to offer a solution that’s right for your business.
Total access and control with WE Connect
Only SD-WAN from Windstream Enterprise comes with WE Connect, a customizable portal that adapts to the way you manage your network. Gain immediate access to all the information about your services, along with the essential functions that help you manage and optimize your network.
Centralized management.
Perform routine operational functions, like adding users or locations, in moments versus days.
Insight Engine.
See aggregated data across all locations to help identify anomalies requiring corrective action.
Real-time visibility.
Get an interactive view of network latency, packet loss and jitter by location, plus tools to customize reports for actionable insights.
Anytime, anywhere, on any device.
Access WE Connect via a mobile device with all the functions of the desktop app.
Get it done right the first time with Professional Services
Relieve your team from tedious site installations and rollouts so they can focus on strategic priorities. Windstream Enterprise offers deep expertise in a broad spectrum of LAN, WAN, UC, voice, security, hybrid IT, cloud and legacy applications and technologies.
To find out more about SD-WAN from Windstream Enterprise, visit the SD-WAN solution page.
10s of 1000s of deployments across the nation and counting.
SD-WAN case studies: See how Windstream Enterprise helps enterprises achieve superior network performance
Windstream Enterprise has helped thousands of enterprise clients across the U.S. drive business transformation with our high-performing SD-WAN ConciergeTM solution and our unrivaled service experience.
Here are 10 SD-WAN case studies that span industry, organizational size, business challenge and solution set that can help you make an informed technology decision for your team and your business.
Discover the Windstream Enterprise vision for cloud networking
Tune in to our podcast series on Top Gun, where our senior product leadership discusses the networking challenges and innovations affecting your business right now.
What makes Windstream Enterprise different?
Mike Flannery, Chief Marketing Officer
Why choose a managed service provider for SD-WAN over doing it yourself.
Mike Frane, VP of Product Management for Network, Security & Digital Experience
Citations
- Valdivia, Gaspar et al. Forecast Analysis: Enterprise Networking Connectivity Growth Trends, Worldwide. September 20, 2019.
- MacDonald, Neil, et al. “2021 Strategic Roadmap for SASE Convergence.” Gartner. March 25, 2021.